Lung transplantation after paraquat poisoning in an adolescent: one case report and literature review
-
摘要:
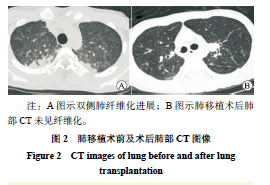
目的 总结百草枯中毒患者中毒后移植时机以及相关处理措施对预后的影响。 方法 回顾性分析1例百草枯中毒行双肺移植术治疗患者的临床资料,总结分析该例患者的临床表现、辅助检查以及诊治经过。 结果 1例17岁青少年在摄入25%百草枯20~30 mL后出现恶心、呕吐、咳嗽伴全身乏力入院。患者经对症支持治疗后,氧饱和情况无改善,肺部纤维化持续进展,遂在体外膜肺氧合(ECMO)辅助下行序贯双侧肺移植。经术后康复治疗,并积极防治并发症,患者于术后50 d出院。 结论 百草枯中毒后的移植时机可选择在肝肾功能开始恢复时,围手术期主动、有针对性地预防潜在致病性细菌感染,以及早期康复训练有助于改善肺移植受者的预后。 Abstract:Objective To summarize the effect of the timing of lung transplantation and related treatment measures on clinical prognosis of patients with paraquat poisoning. Methods Clinical data of a patient with paraquat poisoning undergoing bilateral lung transplantation were retrospectively analyzed. Clinical manifestations, auxiliary examination, diagnosis and treatment of this patient were summarized and analyzed. Results A 17-year-old adolescent was admitted to hospital due to nausea, vomiting, cough and systemic fatigue after oral intake of 20-30 mL of 25% paraquat. After symptomatic support treatment, the oxygen saturation was not improved, and pulmonary fibrosis continued to progress. Therefore, sequential bilateral lung transplantation was performed under extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). After postoperative rehabilitation and active prevention and treatment for postoperative complications, the patient was discharged at postoperative 50 d. Conclusions The timing of lung transplantation after paraquat poisoning may be selected when the liver and kidney function start to recover. Active and targeted prevention of potential pathogen infection in perioperative period and early rehabilitation training contribute to improving clinical prognosis of lung transplant recipients. -
表 1 文献报道的百草枯中毒肺移植受者的临床资料
Table 1. Clinical data of paraquat poisoning lung transplant recipients reported in the literature
研究者 年份 患者年龄
(岁)术前肝
功能术前肾
功能中毒到移植
的时间(d)ECMO使用
时间(d)ECMO
方式肺移植
类型术后生存
时间Matthew H, et al[4] 1968 15 异常 异常 6 -① - 单肺 19 d Cooke NJ, et al[12] 1973 18 异常 异常 10 - - 单肺 12 d 未列出[13] 1985 31 - 异常 19 14 V-V 双肺 110 d Walder B, et al[14] 1997 17 - 异常 44 44 体外循环 单肺 >2年 Jiao GH, et al[15] 2014 24 稳定 稳定 56 44 V-V 双肺 >5年 Jiao GH, et al[15] 2018 45 稳定 稳定 38 38 V-V 双肺 >3年 Jiao GH, et al [15] 2020 38 稳定 稳定 27 27 V-A② 双肺 >7个月 Jiao GH, et al [15] 2021 30 稳定 稳定 28 28 V-V 双肺 >7个月 Tang X, et al[16] 2015 21 恢复 恢复 56 44 V-V 双肺 >1年 Jiang WZ, et al[17] 2019 26 - - 58 35 V-V/V-A 双肺 >1年 Wu Y, et al[18] 2022 18 - - 34 34 - 双肺 >1年 注:①-为文献未报道。
②V-A 为静脉-动脉。 -
[1] MAJIDI M. Therapeutic strategies in managing acute paraquat poisoning: a review study[J]. Int J Med Toxicol Forens Med, 2021, 11(3): 7. DOI: 10.32598/ijmtfm.v11i3.33633. [2] KUMAR S, GUPTA S, BANSAL YS, et al. Pulmonary histopathology in fatal paraquat poisoning[J]. Autops Case Rep, 2021, 11: e2021342. DOI: 10.4322/acr.2021.342. [3] 付国强, 王建宇, 姚家久, 等. 急性百草枯中毒患者血清程序性死亡因子1水平变化及与肺纤维化的相关性[J]. 中国医药, 2021, 16(3): 369-372. DOI: 10.3760/j.issn.1673-4777.2021.03.012.FU GQ, WANG JY, YAO JJ, et al. Changes of serum programmed death-1 level in patients with acute paraquat poisoning and its correlation with pulmonary fibrosis[J]. China Med, 2021, 16(3): 369-372. DOI: 10.3760/j.issn.1673-4777.2021.03.012. [4] MATTHEW H, LOGAN A, WOODRUFF MF, et al. Paraquat poisoning--lung transplantation[J]. Br Med J, 1968, 3(5621): 759-763. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.3.5621.759. [5] 刘明昭, 史灵芝, 杨航, 等. 肺移植术后气道吻合口狭窄的诊治进展[J]. 器官移植, 2021, 12(5): 533-538. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2021.05.005.LIU MZ, SHI LZ, YANG H, et al. Diagnosis and treatment progress on airway anastomotic stenosis after lung transplantation[J]. Organ Transplant, 2021, 12(5): 533-538. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2021.05.005. [6] SUKUMAR CA, SHANBHAG V, SHASTRY AB. Paraquat: the poison potion[J]. Indian J Crit Care Med, 2019, 23(Suppl 4): S263-S266. DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23306. [7] CAO ZX, ZHAO Y, GAO J, et al. Comparison of severity index and plasma paraquat concentration for predicting survival after paraquat poisoning: a meta-analysis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2020, 99(6): e19063. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019063. [8] EIZADI-MOOD N, JABERI D, BAROUTI Z, et al. The efficacy of hemodialysis on paraquat poisoning mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Res Med Sci, 2022, 27: 74. DOI: 10.4103/jrms.jrms_235_21. [9] REN W, CHEN Y, WANG Y, et al. Inhibitory effect of pirfenidone on pulmonary fibrosis in patients with acute paraquat poisoning[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2021, 13(11): 13192-13199. [10] 刘晓曼, 余厚友, 龚晓亮, 等. 连续性肾脏替代治疗联合血液灌流对急性百草枯中毒患者预后的影响及机制[J]. 贵州医科大学学报, 2022, 47(12): 1416-1421,1428. DOI: 10.19367/j.cnki.2096-8388.2022.12.009.LIU XM, YU HY, GONG XL, et al. Effects of continuous renal replacement therapy combined with hemoperfusion on prognosis and cytokine levels of patients with acute paraquat poisoning[J]. J Guizhou Med Univ, 2022, 47(12): 1416-1421,1428. DOI: 10.19367/j.cnki.2096-8388.2022.12.009. [11] 蒲艳, 钟加菊, 彭建明, 等. 敌草快合并百草枯中毒的诊治体会[J]. 中国中西医结合急救杂志, 2022, 29(6): 737-739. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9691.2022.06.021.PU Y, ZHONG JJ, PENG JM, et al. Experience in diagnosis and treatment of diquat and paraquat poisoning[J]. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med Intensive Crit Care, 2022, 29(6): 737-739. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9691.2022.06.021. [12] COOKE NJ, FLENLEY DC, MATTHEW H. Paraquat poisoning. serial studies of lung function[J]. Q J Med, 1973, 42(168): 683-692. [13] Sequential bilateral lung transplantation for paraquat poisoning. a case report. The Toronto Lung Transplant group[J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 1985, 89(5): 734-742. DOI: 10.1016/S0022-5223(19)38729-X. [14] WALDER B, BRÜNDLER MA, SPILIOPOULOS A, et al. Successful single-lung transplantation after paraquat intoxication[J]. Transplantation, 1997, 64(5): 789-791. DOI: 10.1097/00007890-199709150-00026. [15] JIAO G, LI X, WU B, et al. Case report: delayed lung transplantation with intraoperative ECMO support for herbicide intoxication-related irreversible pulmonary fibrosis: strategy and outcome[J]. Front Surg, 2021, 8: 754816. DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.754816. [16] TANG X, SUN B, HE H, et al. Successful extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy as a bridge to sequential bilateral lung transplantation for a patient after severe paraquat poisoning[J]. Clin Toxicol (Phila), 2015, 53(9): 908-913. DOI: 10.3109/15563650.2015.1082183. [17] 蒋文中, 陈育全, 张伊莉, 等. 百草枯中毒肺移植一例报告并文献复习[J]. 中华劳动卫生职业病杂志, 2019, 37(4): 292-296. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9391.2019.04.013.JIANG WZ, CHEN YQ, ZHANG YL, et al. Lung transplantation in patients with paraquat poisoning: a case report and literature review[J]. Chin J Ind Hyg Occup Dis, 2019, 37(4): 292-296. DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-9391.2019.04.013. [18] WU Y, LI N, LI S, et al. Lung transplantation in a woman with paraquat poisoning that led to pulmonary fibrosis-widely reported by the media: a case report[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2022, 101(49): e32263. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032263. [19] RODRIGUEZ-ANTONA C, SAVIEO JL, LAUSCHKE VM, et al. PharmVar GeneFocus: CYP3A5[J]. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2022, 112(6): 1159-1171. DOI: 10.1002/cpt.2563. [20] BIRDWELL KA, DECKER B, BARBARINO JM, et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) guidelines for CYP3A5 genotype and tacrolimus dosing[J]. Clin Pharmacol Ther, 2015, 98(1): 19-24. DOI: 10.1002/cpt.113. [21] HESSELINK DA, BOUAMAR R, ELENS L, et al. The role of pharmacogenetics in the disposition of and response to tacrolimus in solid organ transplantation[J]. Clin Pharmacokinet, 2014, 53(2): 123-139. DOI: 10.1007/s40262-013-0120-3. [22] LIAO M, WANG C, ZHANG M, et al. Insight on immune cells in rejection and infection postlung transplant[J]. Immun Inflamm Dis, 2023, 11(7): e868. DOI: 10.1002/iid3.868. [23] VILLALBA JA, CHEEK-NORGAN EH, JOHNSON TF, et al. Fatal infections differentially involve allograft and native lungs in single lung transplant recipients[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2023,DOI: 10.5858/arpa.2023-0227-OA[Epub ahead of print [24] ZHOU WY, SHEN L, SHI JX, et al. Real-time, random-access organ screening for carbapenem-resistant organisms (CRO) reduces CRO-associated, donor-derived infection mortality in lung transplant recipients[J]. Infection, 2023, DOI: 10.1007/s15010-023-02089-6 [Epub ahead of print [25] 孙小林. ICU病人继发肺部感染的因素及防治[J]. 中外医疗, 2009, 28(15): 25. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0742.2009.15.014.SUN XL. Factors and prevention of secondary pulmonary infection in ICU patients[J]. Chin Foreign Med Care, 2009, 28(15): 25. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0742.2009.15.014. [26] LANGER D, BURTIN C, SCHEPERS L, et al. Exercise training after lung transplantation improves participation in daily activity: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Am J Transplant, 2012, 12(6): 1584-1592. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04000.x. [27] ANDRIANOPOULOS V, GLOECKL R, BOENSCH M, et al. Improvements in functional and cognitive status following short-term pulmonary rehabilitation in COPD lung transplant recipients: a pilot study[J]. ERJ Open Res, 2019, 5(3): 00060-2019. DOI: 10.1183/23120541.00060-2019. [28] ABIDI Y, KOVATS Z, BOHACS A, et al. Lung transplant rehabilitation-a review[J]. Life (Basel), 2023, 13(2): 506. DOI: 10.3390/life13020506. [29] WANG Z, ZHAO B, DENG M, et al. Utility and safety of airway stenting in airway stenosis after lung transplant: a systematic review[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2023, 10: 1061447. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1061447. [30] KIM HH, JO KW, SHIM TS, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and clinical characteristics of airway complications after lung transplantation[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 667. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-27864-1. [31] CRESPO MM. Airway complications in lung transplantation[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2021, 13(11): 6717-6724. DOI: 10.21037/jtd-20-2696. [32] TESHIGAWARA-TANABE H, HAGIHARA M, MATSUMURA A, et al. Passenger lymphocyte syndrome after ABO-incompatible allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; dynamics of ABO allo-antibody and blood type conversion[J]. Hematology, 2021, 26(1): 835-839. DOI: 10.1080/16078454.2021.1986654. [33] MOOSAVI MM, DUNCAN A, STOWELL SR, et al. Passenger lymphocyte syndrome; a review of the diagnosis, treatment, and proposed detection protocol[J]. Transfus Med Rev, 2020, 34(3): 178-187. DOI: 10.1016/j.tmrv.2020.06.004. [34] FUJIMOTO R, NAKAJIMA D, YUTAKA Y, et al. Long-term persisting donor-derived human leukocyte antigen antibody as a possible passenger lymphocyte syndrome following lung transplantation: a case report[J]. Transplant Proc, 2022, 54(7): 1913-1917. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2022.05.031. [35] RAZUK M FILHO, SANTOS SLD, REIS FPD, et al. Use of Octopus™ Tissue Stabilizer for minimal manipulation approach of bronchial anastomosis in lung transplant[J]. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg, 2023, 38(6): e20220413. DOI: 10.21470/1678-9741-2022-0413. [36] VECCHIO M, KOUTSOKERA A, TOUILLOUX B, et al. Bronchial anastomosis dehiscence and stenosis caused by donor-transmitted mycoplasma hominis infection in a lung transplant recipient: case report and literature review[J]. Transpl Infect Dis, 2021, 23(2): e13475. DOI: 10.1111/tid.13475. [37] MUÑOZ-FOS A, MORENO P, GONZÁLEZ FJ, et al. Airway complications after lung transplantation-a contemporary series of 400 bronchial anastomoses from a single center[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12(9): 3061. DOI: 10.3390/jcm12093061. [38] CHAMOGEORGAKIS T, MOQUIN K, SIMOFF M, et al. Repair of bronchial anastomosis following lung transplantation[J]. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2022, 70(6): 527-530. DOI: 10.1055/s-0041-1723002. -





 下载:
下载: