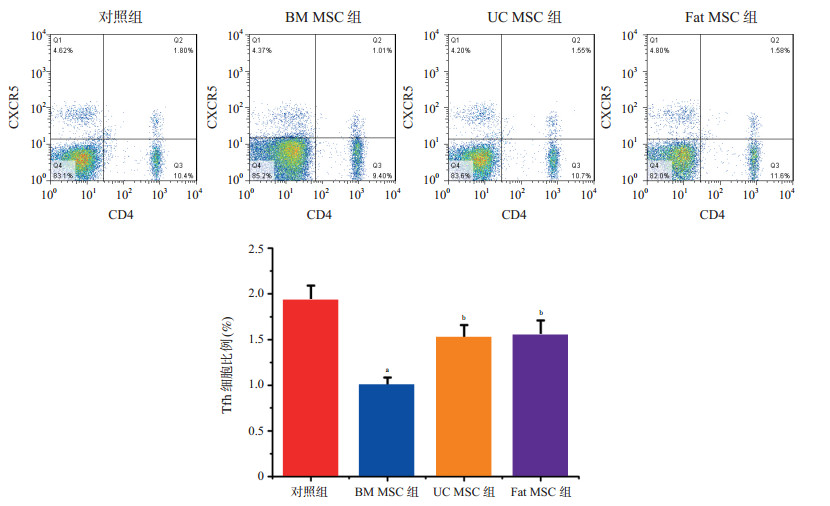
| [1] |
GÓMEZ-MARTÍN D, DÍAZ-ZAMUDIO M, ROMO-TENA J, et al. Follicular helper T cells poise immune responses to the development of autoimmune pathology[J]. Autoimmun Rev, 2011, 10(6): 325-330. DOI: 10.1016/j.autrev.2010.11.007.
|
| [2] |
赵聪, 李宏增, 马超, 等.视神经脊髓炎谱系疾病患者循环滤泡辅助性T细胞和滤泡调节性T细胞的变化[J].实用医学杂志, 2017, 33(3): 379-383. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725. 2017.03.012.ZHAOC,LI HZ, MA C, et al. Changes in circulating follicular helper T cells and regulatory follicular T cells in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder[J]. J Pract Med, 2017, 33(3): 379-383. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2017.03.012.
|
| [3] |
CHTANOVA T, TANGYE SG, NEWTON R, et al. T follicular helper cells express a distinctive transcriptional profile, reflecting their role as non-Th1/Th2 effector cells that provide help for B cells[J]. J Immunol, 2004, 173(1): 68-78. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.1.68
|
| [4] |
LI H, PAUZA CD. CD25(+) Bcl6(low) T follicular helper cells provide help to maturing B cells in germinal centers of human tonsil[J]. Eur J Immunol, 2015, 45(1): 298-308. DOI: 10.1002/eji.201444911.
|
| [5] |
LINTERMAN MA, VINUESA CG. Signals that influence T follicular helper cell differentiation and function[J]. Semin Immunopathol, 2010, 32(2): 183-196. DOI: 10.1007/s00281-009-0194-z.
|
| [6] |
DE MIGUEL MP, FUENTES-JULIÁN S, BLÁZQUEZ-MARTÍNEZ A, et al. Immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stem cells: advances and applications[J]. Curr Mol Med, 2012, 12(5): 574-591. doi: 10.2174/156652412800619950
|
| [7] |
ZHANG X, HIRAI M, CANTERO S, et al. Isolation and characterization of mesenchymal stem cells from human umbilical cord blood: reevaluation of critical factors for successful isolation and high ability to proliferate and differentiate to chondrocytes as compared to mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2011, 112(4): 1206-1218. DOI: 10.1002/jcb.23042.
|
| [8] |
HEO JS, CHOI Y, KIM HS, et al. Comparison of molecular profiles of human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, placenta and adipose tissue[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2016, 37(1): 115-125. DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2413.
|
| [9] |
CAGLIANI J, GRANDE D, MOLMENTI EP, et al. Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stromal cells and their clinical applications[J]. J Stem Cell Regen Biol, 2017, 3(2). DOI: 10.15436/2471-0598.17.022.
|
| [10] |
SALINAS TEJEDOR L, SKRIPULETZ T, STANGEL M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells require the peripheral immune system for immunomodulating effects in animal models of multiple sclerosis[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2016, 11(1): 90-91. DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.175050.
|
| [11] |
CHOI YS, KAGEYAMA R, ETO D, et al. ICOS receptor instructs T follicular helper cell versus effector cell differentiation via induction of the transcriptional repressor Bcl6[J]. Immunity, 2011, 34(6): 932-946. DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.03.023.
|
| [12] |
JIA Y, ZENG Z, LI Y, et al. Impaired function of CD4+ T follicular helper (Tfh) cells associated with hepatocellular carcinoma progression[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(2):e0117458. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117458.
|
| [13] |
ZHANG X, ING S, FRASER A, et al. Follicular helper T cells: new insights into mechanisms of autoimmune diseases[J]. Ochsner J, 2013, 13(1): 131-139. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=24efe1558710c98ab25ad0f31388720f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
|
| [14] |
梁嘉晖, 沈娟, 罗茜, 等.环孢素A对人扁桃体Tfh细胞产生IL-21以及对CD40L和Bcl-6表达的抑制作用[J].热带医学杂志, 2016, 16(4):423-429.LIANG JH, SHEN J, LUO Q, et al. Suppressive effects of CsA on the production of IL-21 and the expression of CD40L and Bcl-6 in tonsillar Tfh cells[J]. J Trop Med, 2016, 16(4):423-429.
|
| [15] |
WOLK K, SABAT R. Interleukin-22: a novel T-and NK-cell derived cytokine that regulates the biology of tissue cells[J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2006, 17(5): 367-380. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2006.09.001
|
| [16] |
NIU J, YUE W, LE-LE Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit T cell activation by releasing TGF-β1 from TGF-β1/GARP complex[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(59): 99784-99800. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.21549.
|
| [17] |
ENGLISH K. Mechanisms of mesenchymal stromal cell immunomodulation[J]. Immunol Cell Biol, 2013, 91(1): 19-26. DOI: 10.1038/icb.2012.56.
|
| [18] |
PRASANNA SJ, GOPALAKRISHNAN D, SHANKAR SR, et al. Pro-inflammatory cytokines, IFNgamma and TNFalpha, influence immune properties of human bone marrow and Wharton jelly mesenchymal stem cells differentially[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(2): e9016. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009016.
|
| [19] |
BASSI ÊJ, DE ALMEIDA DC, MORAES-VIEIRA PM, et al. Exploring the role of soluble factors associated with immune regulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Stem Cell Rev, 2012, 8(2): 329-342. DOI: 10.1007/s12015-011-9311-1.
|





 下载:
下载: