Study on clinicopathologic characteristics and individualized immunotherapy of antibody-mediated rejection after renal transplantation
-
摘要:
目的 探讨肾移植后抗体介导的排斥反应(AMR)的临床病理特征与个体化免疫治疗策略及预后。 方法 回顾性分析2010年1月至2013年12月, 在河南中医学院第一附属医院泌尿外科肾移植科收治的32例肾移植术后经病理确诊的AMR患者的临床资料。根据不同患者的临床病理特点, 采取相应的免疫干预措施, 分别于治疗前及治疗后测定肾功能、群体反应性抗体(PRA)及血清免疫球蛋白(Ig)G、IgA、IgM水平, 并观察不良反应。 结果 本组患者中急性抗体介导的排斥反应(AAMR)18例, 慢性抗体介导的排斥反应(CAMR)14例; PRA阳性患者13例, 其中8例(62%, 8/13)为供体特异性抗体, 5例(38%, 5/13)为非供体特异性抗体。早期AAMR的主要病理表现为急性肾小管坏死(ATN)样改变, 管周毛细血管炎及小球炎, 动脉纤维素样坏死, C4d在肾小管周围毛细血管(PTC)呈线性沉积, 免疫球蛋白或C3在动脉壁沉积。CAMR的病理表现为肾小球病样改变, PTC基底膜分层, 动脉内膜纤维增厚, C4d在PTC弥漫沉积。经治疗, 肾功能恢复正常20例(63%, 20/32), 肾功能稳定7例(22%, 7/32), 血清肌酐(Scr)呈缓慢升高5例(16%, 5/32), 其中2例(2/5)回归血液透析, 3例(3/5)尚不需透析治疗, 无1例死亡。治疗后血尿素氮(BUN)、Scr、PRA及血清IgG、IgA、IgM较治疗前明显降低(均为P < 0.01)。治疗期间未见严重不良反应。 结论 肾移植术后AMR可表现为AAMR或CAMR。AMR诊断的金标准是移植肾病理活组织检查, 治疗AMR的关键措施是及时采取有效的个体化免疫治疗方案。 Abstract:Objective To investigate clinicopathologic characteristics, individualized immunotherapy and prognosis of antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) after renal transplantation. Methods Clinical data of 32 patients, who were confirmed as AMR after renal transplantation by pathology and admitted in the Department of Urology and Renal Transplantation of the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan Traditional Medical College from January 2010 to December 2013, were retrospectively studied. The corresponding immunological intervention was adopted according to the clinicopathologic characteristics of different patients. The indicators including renal function, panel reactive antibody (PRA) and serum immunoglobulin (Ig) G, IgA and IgM level before and after treatment were determined, and adverse reactions were observed. Results Of all 32 patients, 18 developed acute antibody-mediated rejection (AAMR) and 14 developed chronic antibody-mediated rejection (CAMR). Of 13 PRA-positive patients, 8 (62%, 8/13) cases were with donor specific antibody and 5 (38%, 5/13) cases were with non-donor specific antibody. The primary pathological manifestations of early AAMR were changes of acute tubular necrosis (ATN), peritubular capillary inflammation, glomerulitis, fibrinoid necrosis of small arteries, linear C4d deposition in peritubular capillaries (PTC) and immunoglobulin or C3 deposition in arterial wall. The pathological manifestations of CAMR were changes of glomerulopathy, splitting of PTC basement membrane, fibrous intimal thickening and diffuse C4d deposition in PTC. After treatment, the renal function of 20 (63%, 20/32) patients returned to normal, the renal function of 7 (22%, 7/32) patients were stable, the serum creatinine (Scr) of 5 (16%, 5/32) patients increased slowly. Of such 5 patients, 2 (2/5) patients continued hemodialysis, 3 (3/5) patients did not need hemodialysis and no patient died. The indicators including blood urea nitrogen (BUN), Scr, PRA and serum IgG, IgA and IgM after treatment decreased significantly when compared with those before treatment (all in P < 0.01). No serious adverse reaction was noted during the treatment. Conclusions AMR may manifest as AAMR or CAMR after renal transplantation. The gold standard for diagnosing AMR is pathologic biopsy of transplant kidney. To adopt effective individualized immunotherapy in time is the critical measure for treatment of AMR. -
Key words:
- Renal transplantation /
- Antibody-mediated rejection /
- Pathology /
- Individualized therapy
-
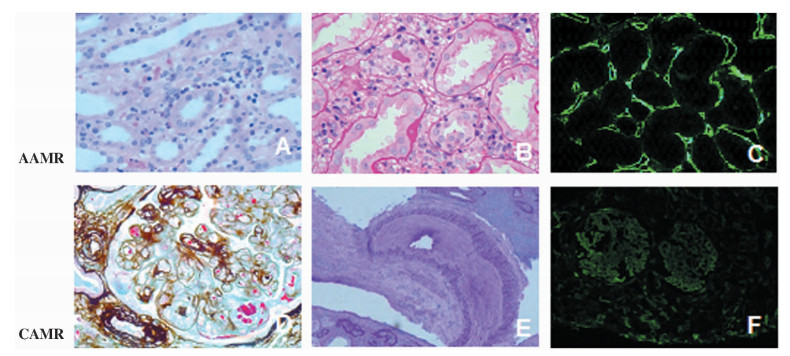
图 1 抗体介导的排斥反应患者的移植肾组织病理学表现
注:A~C图为AAMR病理表现。A图为管周毛细血管内单个核细胞、嗜酸性粒细胞浸润(HE,×400);B图为小管间质单个核细胞浸润、水肿及小管炎(PAS,×400);C图为PTC,见C4d沉积(免疫荧光,×400)。D~F图为CAMR病理表现。D图显示小球毛细血管基膜不规则增厚、分层,内皮细胞肿胀、增生,内皮下见纤维素、红细胞碎屑(PASM-Masson,×400);E图显示弓形血管分支内膜中度纤维性增厚,周围小管萎缩、间质纤维化和灶性单个核细胞浸润(PAS,×200);F图显示PTC小球和毛细血管壁C4d阳性(免疫荧光,×200)
Figure 1. The histopathological changes of transplant kidney of patients with antibody-mediated rejection
表 1 抗体介导的排斥反应患者治疗前后相应参数变化
Table 1. The corresponding parameters of patients with antibody-mediated rejection before and after treatment(x±s)
组别 时间点 n BUN
(mmol/ L)Scr
(μmol/L)PRA
(%)IgG
(g/L)IgA
(g/L)IgM
(g/L)AAMR组 治疗前 18 24±7 391±99 39±15 14.2±2.2 5.4±1.2 1.36±0.58 治疗后 18 10±4a 95±44a 15±5a 4.5±1.7a 2.6±1.0a 0.59±0.21a CAMR组 治疗前 14 21±7 365±90 33±13 15.7±6.3 6.3±1.4 1.44±0.62 治疗后 14 11±4a 120±32a 15±6a 6.5±2.1a 3.1±0.8a 0.63±0.19a 注:与同组治疗前比较,aP < 0.01 -
[1] Alvarez-Márquez A, Aguilera I, Gentil MA, et al. Donor-specific antibodies against HLA, MICA, and GSTT1 in patients with allograft rejection and C4d deposition in renal biopsies[J]. Transplantation, 2009, 87(1):94-99. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e31818bd790 [2] 孙启全, 季曙明.抗体介导的移植肾排斥[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志, 2006, 15:282-289. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/szbytxsyzzz200603017Sun QQ, Ji SM. Antibody-mediated rejection[J]. Chin J Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2006, 15:282-289. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/szbytxsyzzz200603017 [3] Seveso M, Bosio E, Ancona E, et al. De novo anti-HLA antibody responses after renal transplantation:detection and clinical impact[J]. Contrib Nephrol, 2009, 162:87-98. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19001816 [4] Melk A, Schmidt BM, Braun H, et al. Effects of donor age and cell senescence on kidney allograft survival[J]. Am J Transplant, 2009, 9(1):114-123. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19133932 [5] Randhawa PS, Schonder K, Shapiro R, et al. Polyomavirus BK neutralizing activity in human immunoglobulin preparations[J]. Transplantation, 2010, 89(12):1462-1465. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3181daaaf1 [6] Wang D, Xu TZ, Chen JH, et al. Factors influencing second renal allograft survival:a single center experience in China[J]. Transpl Immunol, 2009, 20(3):150-154. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2008.09.010 [7] Sis B, Mengel M, Haas M, et al. Banff' 09 meeting report:antibody mediated graft deterioration and implementation of Banff working groups[J].Am J Transplant, 2010, 10(3):464-471. doi: 10.1111/ajt.2010.10.issue-3 [8] Kidney Disease:Improving Global Outcomes(KDIGO) Transplant Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the care of kidney transplant recipients[J]. Am J Transplant, 2009, 9(Suppl 3):S1-S155. http://kdigo.org/home/guidelines/care-of-the-kidney-transplant-recipient/ [9] Jirasiritham S, Khunprakant R, Techawathanawanna N, et al. Treatment of simultaneous acute antibody-mediated rejection and acute cellular rejection with alemtuzumab in kidney transplantation:a case report[J]. Transplant Proc, 2010, 42(3):987-989. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2010.03.018 [10] Obeidat MA, Luyckx VA, Grebe SO, et al. Post-transplant nuclear renal scans correlate with renal injury biomarkers and early allograft outcomes[J].Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2011, 26(9):3038-3045. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfq814 [11] Günther OP, Lin D, Balshaw RF, et al. Effects of sample timing and treatment on gene expression in early acute renal allograft rejection[J].Transplantation, 2011, 91(3):323-329. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3182029b16 [12] Haas M, Sis B, Racusen LC, et al. Banff 2013 meeting report:inclusion of c4d-negative antibody-mediated rejection and antibody-associated arterial lesions[J]. Am J Transplant, 2014, 14(2):272-283. doi: 10.1111/ajt.12590 [13] 王仁定, 王慧萍, 吴建永, 等.急性细胞性排斥伴补体裂解片断C4d沉积对移植肾预后的影响[J].器官移植, 2010, 1(3):141-143, 165. http://www.organtranspl.com/browse/detail/qkid/33/id/404Wang RD, Wang HP, Wu JY, et al. Effect of acute cellular rejection with C4d deposition on renal allograft survival[J].Organ Transplant, 2010, 1(3):141-143, 165. http://www.organtranspl.com/browse/detail/qkid/33/id/404 [14] Singh N, Pirsch J, Samaniego M. Antibody-mediated rejection:treatment alternatives and outcomes[J].Transplant Rev, 2009, 23(1):34-46. doi: 10.1016/j.trre.2008.08.004 [15] 孙启全, 黎磊石, 唐政, 等.他克莫司联合霉酚酸酯治疗肾移植术后早期难治性急性体液性排斥的疗效[J].肾脏病与透析肾移植杂志, 2006, 1(15):12-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZBY200601002.htmSun QQ, Li LS, Tang Z, et al. The efficacy of FK506 and mycophenolate mofetil rescue therapy for acute humoral rejection of kidney transplants[J]. Chin J Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2006, 1(5):12-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZBY200601002.htm -





 下载:
下载: